Table: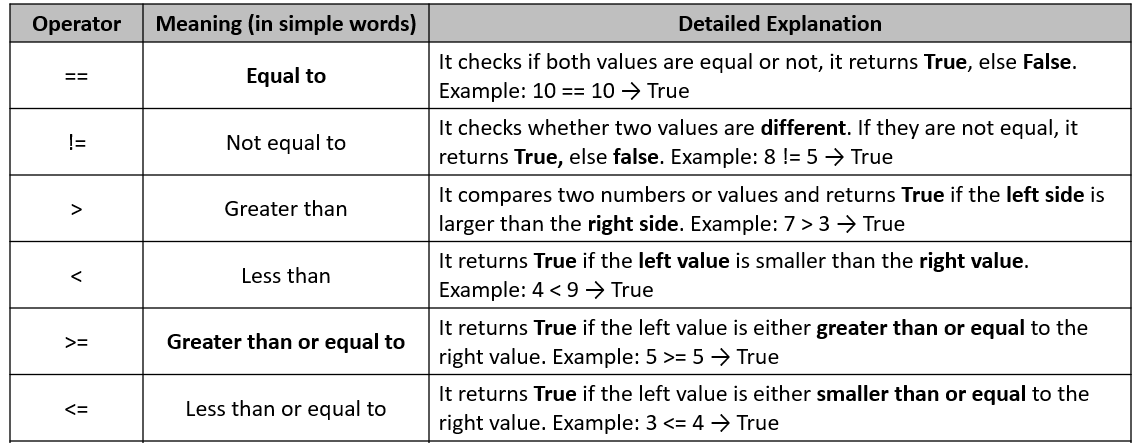
Example 1: Equal to and Not Equal to Operators
In Python language, comparison operators like == (equal to) and! = (not equal to) are used when we need to compare two values.
These operators are commonly used in multiple scenarios like login systems, authentication checks, and validation processes.
Let’s try to understand it with the help of a simple example:
password = "admin"
user_input = "admin"
if user_input == password:
print("Access granted")
else:
print("Wrong password ")Output:
Access granted
Example 2: Greater Than or Less Than Operators
The > (greater than) and < (less than) operators (both) are used to compare numerical values.
They help in decision-making in real life scenarios - for example, comparing scores, prices, or ages.
Let’s look at a simple example to understand how they work:
battery_percentage = 18
if battery_percentage < 20:
print("Low battery - please charge")
else:
print("Battery level sufficient")Output:
Low battery - please charge
This program checks if the battery percentage is less than 20; since it’s 18, it prints “Low battery – please charge.
Example 3: Greater Than or Equal / Less Than or Equal Operators
In Python, greater than or equal to (>=) and less than or equal to (<=) operators are also used to compare numerical values and they also include boundary values while comparing numbers.
temperature = 30
if temperature >= 35:
print("High temperature alert")
elif temperature <= 15:
print("Low temperature alert")
else:
print("Temperature is normal")Output:
Temperature is normal
Real-World Examples:
In real life, comparison operators help programs make smart choices.
For example, an online shopping application can easily check if a product’s price is within your budget (like shown below) before letting you buy it:
Example:
product_price = 999
budget = 1000
if product_price <= budget:
print("You can buy this product")
else:
print("Try a cheaper option")Output:
You can buy this product
a) In finance and HR-based applications, they help to evaluate conditions before giving final approvals or ratings.
b) Comparison operators are used in e-commerce websites to check if the price > 10,000, then apply discounts automatically.
Why It Matters:
1. Comparison operators make your program capable of decision-making.
2. Comparison operators give real meaning to conditions.
Learn more about Logical Operators in our “Python Logical Operators” chapter.
