In Python, logical operators allow you to work with multiple conditions in a single line.
It helps you to make your code clean and easier to understand.
There are three types of logical operators in Python language which help you to write complex logic efficiently:
• and
• or
• not
Operator Table:
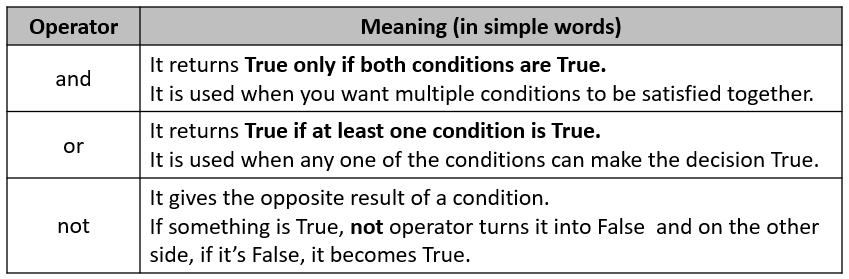
1. and Operator:
In Python, the and operator helps you to write multiple conditions (two or more) in a single statement.
It returns True only if all conditions are True, otherwise it will return false value.
Example:
age = 22
has_license = True
if age >= 18 and has_license:
print("You are allowed to drive")
else:
print("Driving not permitted")Output:
You are allowed to drive
The above program checks the following two conditions:
• Whether the person is 18 years or older.
• Whether the person has a valid driving license or not.
Since both the mentioned conditions are true, the program prints the following output:
You are allowed to drive.
2. or Operator:
In Python, the or operator helps you to write multiple conditions (two or more) in a single statement.
It returns True if any one of them is True., otherwise it will return false value.
Example:
has_id_card = False
has_admit_card = True
if has_id_card or has_admit_card:
print("You can enter the exam hall")
else:
print("Entry not allowed ")Output:
You can enter the exam hall
The above program checks the following two conditions:
• Whether the student has an ID card.
• Or whether the student has an admit card.
Since one of the conditions is True, the program prints the following output:
You can enter the exam hall
3. not Operator:
In Python, the not operator is used to reverse the result of a condition. If a condition is True, not makes it False, and if it’s False, it becomes True.
Example:
is_logged_in = False
if not is_logged_in:
print("Please log in to continue")
else:
print("Welcome back!")Output:
Please log in to continue
The above program checks whether the user is not logged in.
Since is_logged_in is set to False initially, the condition not is_logged_in becomes True.
Therefore, it prints the message:
Please log in to continue
Real-World Examples:
In real world applications, logical operators are used in multiple scenarios like:
a) they are used to authenticate if user login details are correct or not
b) In fraud detection application, they are used to check if multiple risk factors are true or not (at the same time)
c) It is used to automate decisions based on combined conditions in Business Rule Engines
Example: Payment System - Fraud Detection Check
transaction_verified = False
account_flagged = True
if not transaction_verified and account_flagged:
print("Transaction blocked: possible fraud detected.")
else:
print("Transaction approved.")Output:
Transaction blocked: possible fraud detected.
This above program basically checks two things (as mentioned below):
• If the transaction is not verified.
• And if the account is marked as risky.
If both are True, it blocks the transaction to stop possible fraud.Otherwise, it approves the transaction normally
This type of logic is commonly used in banking and fintech applications, where system automatically detects and blocks suspicious activities using simple logical operators like not, and, and or.
Why It Matters
• Logical operators are used to build multi-condition intelligence in a software application.
• They are also used in AI pipelines, data filters, and automated decision systems.
• They make your code cleaner, compact, and more readable.
